Mold is not a plant and not an animal.
Mold is a fungi with its own unique “lifestyle”.
Green plants make their own food using carbon dioxide from air and water through photosynthesis, while producing oxygen. A great blessing for all living creatures.
1. Contrary to green plants, the food sources for mold are carbon hydrates extracted from the material the mold lives on. As mold extracts carbon, it destroys the carbon-containing substances: organic materials such as wood, wood-based products and plastics made from petroleum products as well as building materials such as concrete and sheetrock. Other examples are paper products, card board, paints, insulation, carpets and upholstery. Mold infestations can have catastrophic consequences by weakening or destroying structural elements in buildings. 
2. But the destruction of materials is not all. While digesting its food, mold releases toxic compounds into the air, which present a health hazard to humans living in mold infested houses.
3. And that is still not all. One mold colony can grow millions of spores to reproduce. When the tiny spores are airborne and dispersed throughout a building, they are inhaled by the people living in the building causing coughing, allergic reactions or asthma. People have become seriously ill from living in moldy places. The smell alone can be bad.
Not all fungi are as unwanted as mold. Some are great decomposers, where decomposition is wanted. For example, when trees are dead and slowly turned to earth. Antibiotics such as Penicillin are fungi. Their development has been a blessing for people. Even in our food we welcome the distinctive taste of the yeast-fungi when brewing or baking.
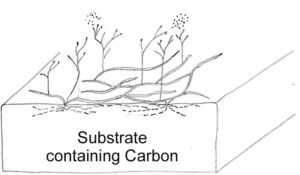
Mold grows as tiny microorganisms on wood, sheet rock and most all building materials. The problem starts with a tiny spore, which can wait for years to find the right conditions to grow.
Once the spore develops into a fungi, the fungi occupies 4 levels:
– Penetrates through and under the surface into the substrate looking for food.
– Develops an ever extending web creeping along the surface as long as favorable conditions exists.
– Spore-producing extensions grow vertically up. The ends swell and spores are produced.
– When the spores are ready, they are air borne by the millions and dispersed in the surrounding air. The slightest drift can carry the spores far away in a short time, where they will, if conditions allow start growing a new colony.
Summary:
Spores can be found anywhere. Spores need four ingredients to start growing:
- food (material containing carbons)
- humidity from water
- oxygen from air
- moderate temperatures.
If all these ingredients are plenty-full available, spores will grow and start new mold colonies. Since we cannot eliminate the air in buildings nor can we eliminate materials containing carbons nor do we want to live in freezing temperatures, we can only try to keep the moisture in materials and in the air low enough so that mold cannot develop.
What to do to prevent mold?
To avoid mold growth, the humidity levels should be kept as low as possible day and night, preferably not above 50%. (gov.moldguide). In many cases, that is the only way you can control mold growth. If the air stays within these limits, wood, drywall and other materials will also keep a low enough moisture content.
If exposed to water, building materials will absorb moisture and moisture levels quickly become higher than the mold threshold. Keeping the air humidity low and drying-out the materials as fast as possible, will help prevent mold growth with all the undesirable consequences for the health of humans and the health of materials.
→ Lignomat’s Thermo-Hygrometers
→ Lignomat’s Pin Meters
→ Lignomat’s Pinless Meters
Moisture Meters for Building Maintenance

